Useaking’s
Plan
Bangladesh
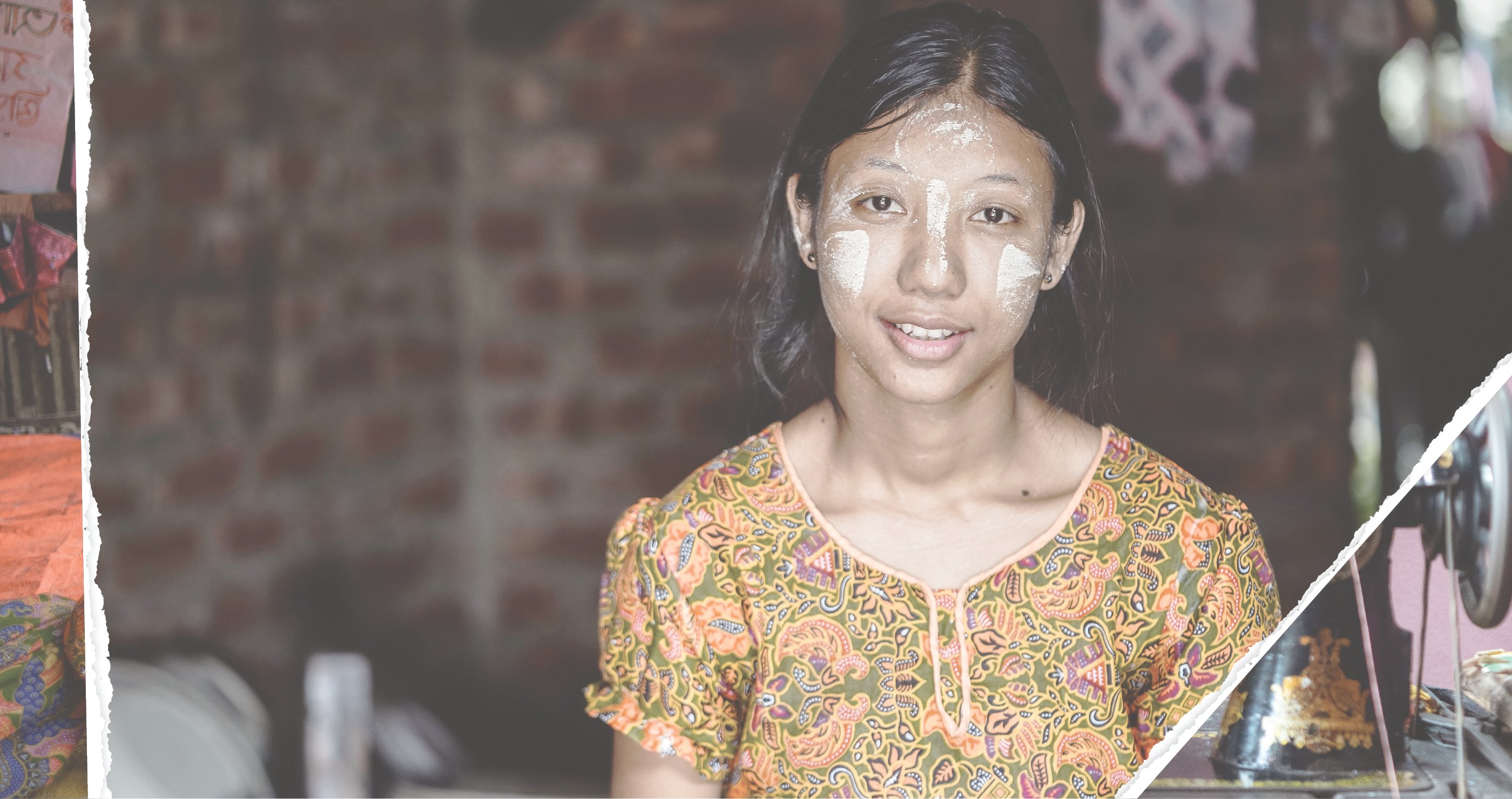
In the community of Cox’s Bazar in Bangladesh, 21-year-old Useaking, a mother of two, can pinpoint the event that changed her life forever: getting her period.
“I used to have to stay home for days when I had my period,” says Useaking, whose information on menstruation came from myths and taboos. “I didn’t even know to use rags, let alone sanitary pads, so I couldn’t go out as people would see my bloodstained clothes.”
Staying home, in turn, affected her education. She fell behind in school.
As her studies slipped away, so did her options. Useaking was 17 when she dropped out of school, against her parents’ wishes, to marry a boy she’d met at Sangrai, a traditional water festival. She thought marriage would bring her the freedom she craved.
But with marriage came an early pregnancy.
Alone in a new community, Useaking was expecting her first child by age 18. Her second arrived 14 months later. “At the time, I didn’t know I could use the health services in my area. No one told me about this or was there to guide me,” she recalls, describing a situation that is common in many parts of Bangladesh, where 22% of girls marry before the age of 15.
Lift the veil off early marriage


Watch
Useaking's
story
Useaking’s Plan
Advocate
to end early
and forced marriage.
Educate
girls about
their rights.
Create
a better
future for her daughter.





By the Numbers
• Bangladesh ranks among the top 10 countries in the world with the highest levels of child, early and forced marriage.







• Bangladesh ranks among the top 10 countries in the world with the highest levels of child marriage.
• Child marriage is illegal in Bangladesh, but there are still 38 million child brides, including women who were first married in childhood. Of them, 13 million girls were married before the age of 15.
• Some families agree to marry their underage daughters due to economic pressures or the belief that marriage will protect them from harassment and sexual assault. For others, it’s a way to control girls’ sexuality, mobility, access to information and opportunities to make their own life choices.
• While dowry is illegal in Bangladesh, it is widely practised. Dowry increases as girls age and is another driver for early forced marriage.
• Married girls are four times more likely not to finish school and are more likely to experience complications from pregnancy and childbirth and be exposed to gender-based violence. They also tend to have less influence on household decisions, including what health care they and their children can access.
• Early and forced marriage begins to decline only among those with at least 10 years of schooling. The incidence falls below 50% among those with at least 12 years of schooling.
• Early marriage (before age 18) is a risk factor for intimate partner violence (IPV) against women. Worldwide, Bangladesh has the highest prevalence of IPV and very early marriage (before age 15).
• Early and forced marriage is becoming less common in Bangladesh. The prevalence of marriage by age 18 has dropped, from over 90% around 1970 to just over 50% today.
• If the rate of decline observed over the past 10 years were to double, the prevalence of child marriage in Bangladesh would drop to about 30% by 2030 and to less than 15% by 2050.
• Meeting the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) target to end child marriage by 2030 (and the national target to end child marriage by 2041) will require a significant push. Progress must be at least eight times faster than the rate observed over the past decade to meet the national target and 17 times faster to meet the SDG target.
• Child marriage is illegal in Bangladesh, but there are still 38 million child brides, including women who were first married in childhood. Of them, 13 million girls were married before the age of 15.
• Some families agree to marry their underage daughters due to economic pressures or the belief that marriage will protect them from harassment and sexual assault. For others, it’s a way to control girls’ sexuality, mobility, access to information and opportunities to make their own life choices.
• While dowry is illegal in Bangladesh, it is widely practised. Dowry increases as girls age and is another driver for early forced marriage.
• Married girls are four times more likely not to finish school and are more likely to experience complications from pregnancy and childbirth and be exposed to gender-based violence. They also tend to have less influence on household decisions, including what health care they and their children can access.
• Child, early and forced marriage begins to decline only among those with at least 10 years of schooling. The incidence falls below 50% among those with at least 12 years of schooling.

• Early marriage (before age 18) is a risk factor for intimate partner violence (IPV) against women. Worldwide, Bangladesh has the highest prevalence of IPV and very early marriage (before age 15).
• Child, early and forced marriage is becoming less common in Bangladesh. The prevalence of marriage by age 18 has dropped, from over 90% around 1970 to just over 50% today.
• If the rate of decline observed over the past 10 years were to double, the prevalence of child marriage in Bangladesh would drop to about 30% by 2030 and to less than 15% by 2050.
• Meeting the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) target to end child marriage by 2030 (and the national target to end child marriage by 2041) will require a significant push. Progress must be at least eight times faster than the rate observed over the past decade to meet the national target and 17 times faster to meet the SDG target.




2050

Useaking’s plan came together with the support of our LEAP (Lifting Healthy, Empowered and Protected Girls and Women in Cox’s Bazar) program and our key funder, Global Affairs Canada. The goal of the program is to work with adolescent girls and young women living in host communities and refugee camps and help them realize and advocate for their sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR).
The central focus is helping prevent child, early and forced marriage and gender-based violence and improving access to information and health services. This three-year program, which was launched in 2022, will reach 97,773 adolescent girls and boys ages 10 to 24.
How Plan International Helped
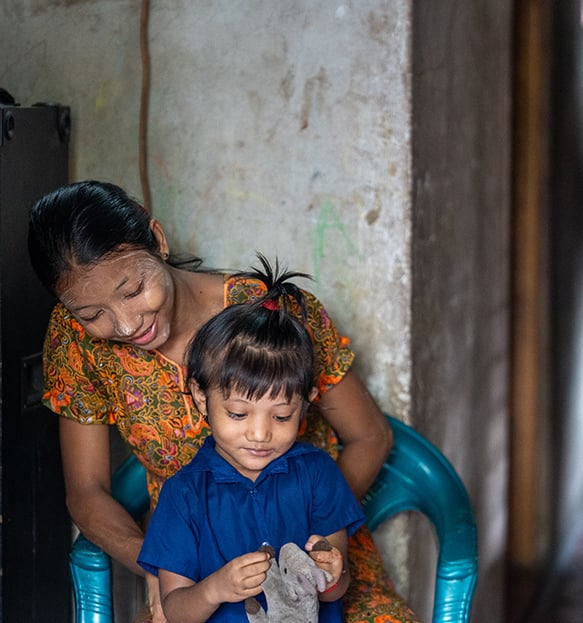
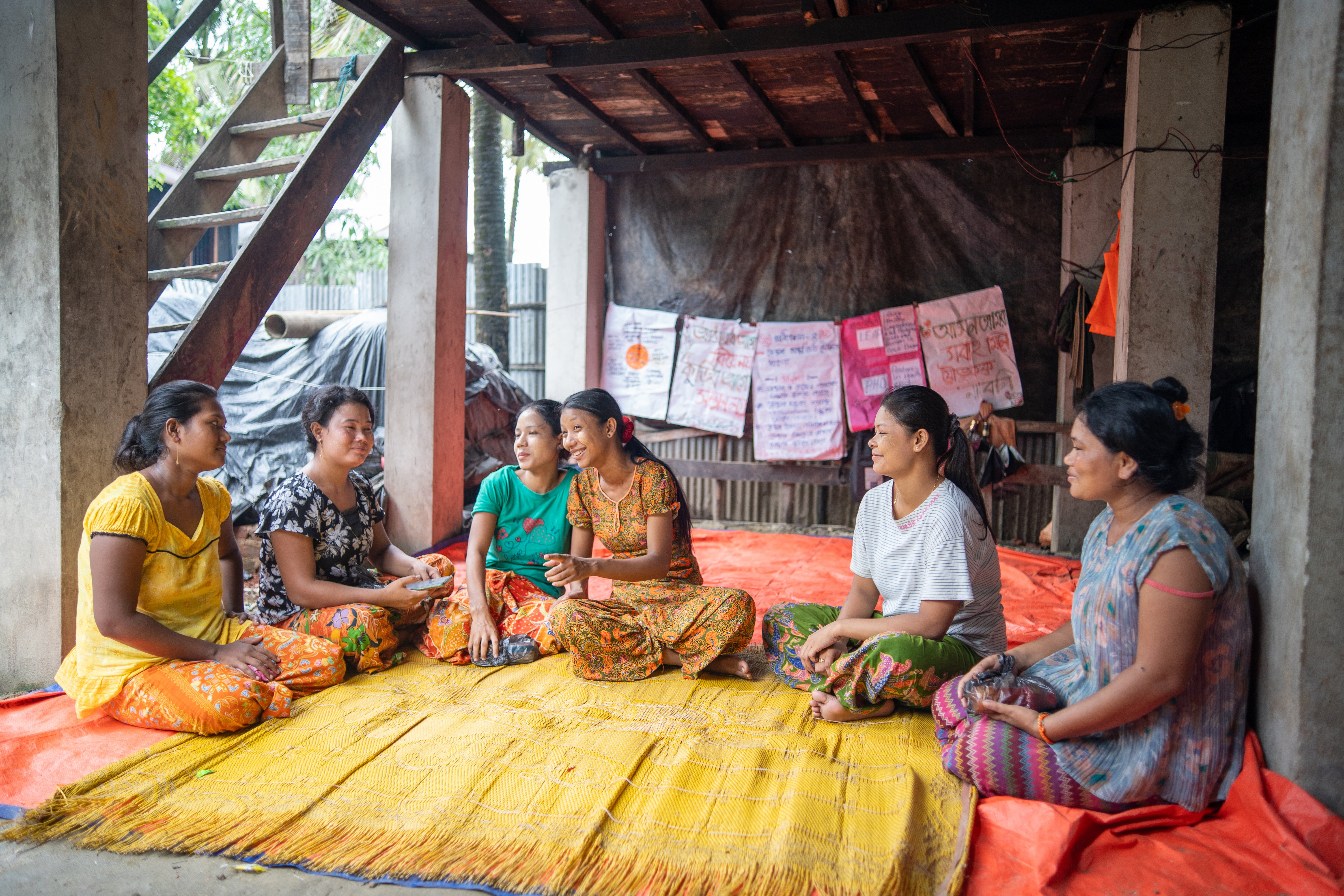
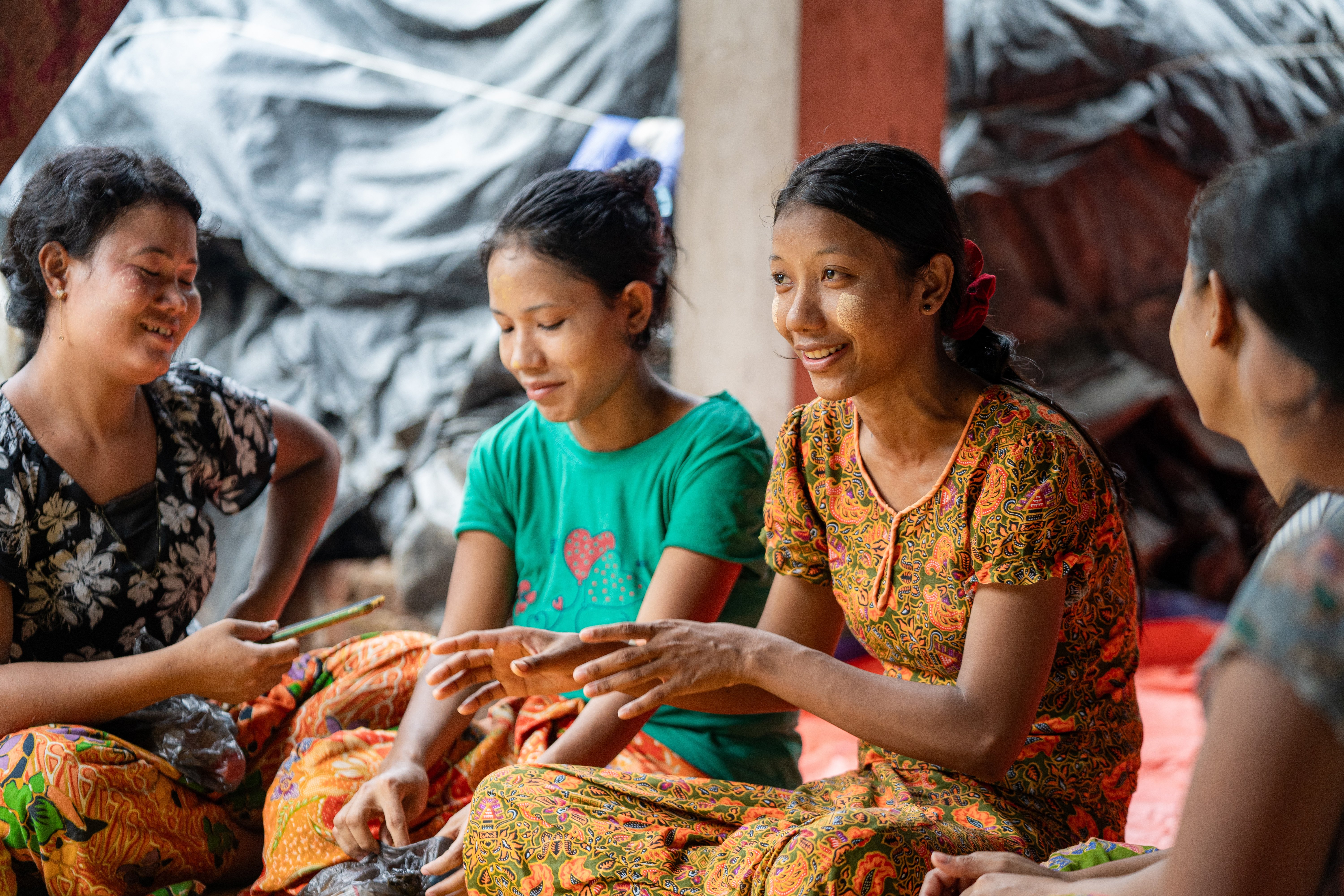
Useaking is a mentor in one of the young married women‘s groups organized by Plan International. They talk about issues related to sexual and reproductive health and rights.
Useaking’s story took an unexpected turn when she discovered a community support group for young married women. Among her new friends, she learned about sexual and reproductive health, mental health and gender-based violence. The more she learned about her rights and the importance of family planning, the more confident - and vocal - she became.
Determined to share her knowledge with any girl who would listen, including her younger sister, Useaking began speaking out against early and forced marriage, using her life as an example. “[Girls who study and work] can live freely and go wherever they want,” she says. “But I cannot. If I had known, I might have made different choices.”
Given that daughters of teenage mothers run a greater risk of becoming young mothers themselves, Useaking has a vested interest in breaking the cycle of intergenerational poverty that perpetuates early marriage: “I want my daughter to reach her full potential and enjoy her freedom, to have access to education and the opportunity to pursue her dreams.”



1
2

Photography by Tanveer Abid

A different path
Useaking’s number-one piece of advice: “I tell my girlfriends and girls around me to study or learn a job without getting married at a young age like me.”

Useaking is one of 2,100 participants in the young married women’s groups. Trained as a LEAP female mentor, Useaking now meets with adolescent girls and boys to help them understand and advocate for their SRHR. The LEAP project also offers training for service providers, women’s organizations and government agencies on advocating for and delivering sexual and reproductive health services to adolescents and young women.







Words by Katherine Gougeon | Reading time: 5 minutes
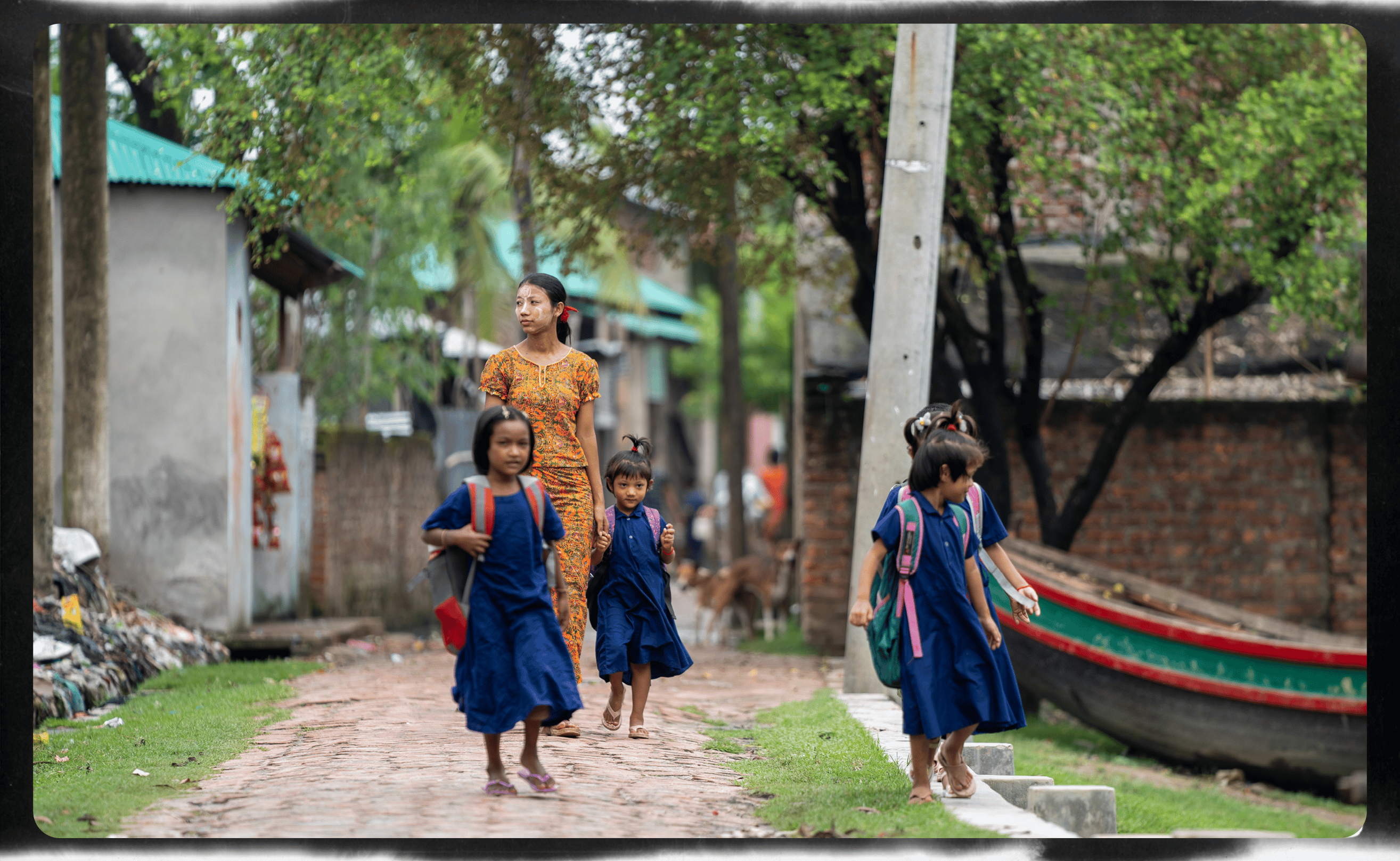
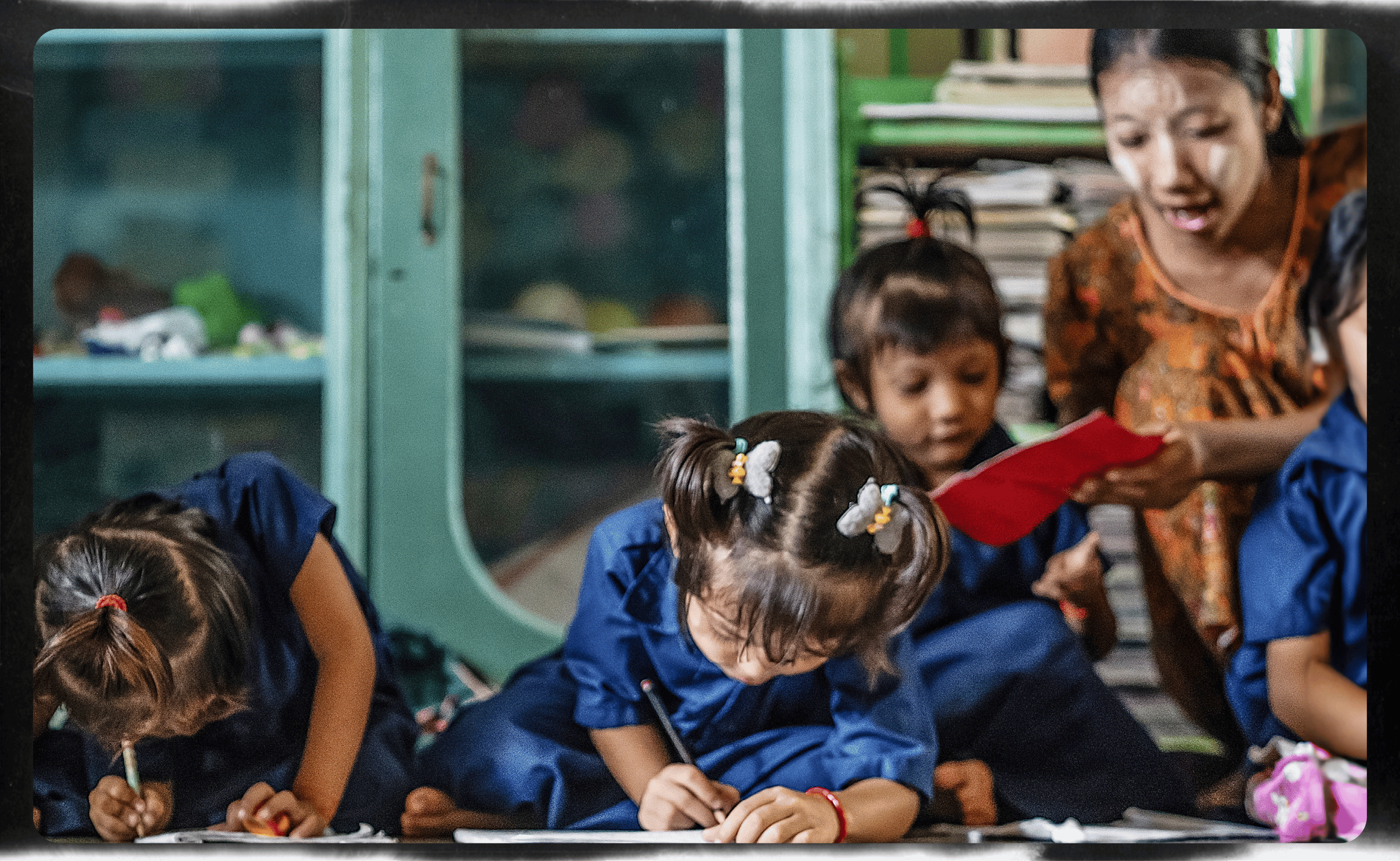
Class time
Useaking takes her daughter to school each day and enjoys spending time in the classroom with her. Married girls are four times more likely not to finish school. In Useaking’s case, she dropped out after missing too many classes when she had her period.
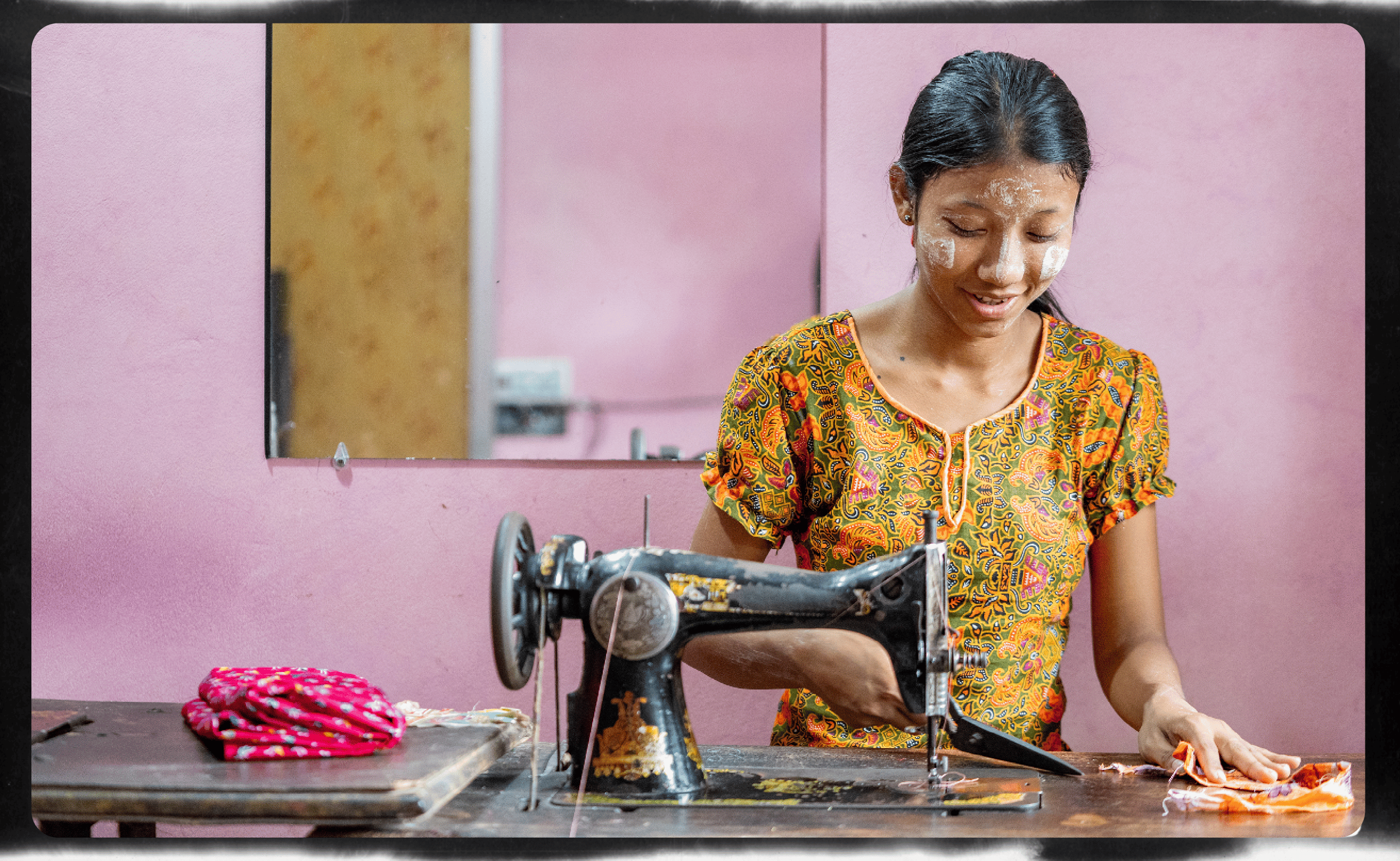
A stitch at a time
If she had continued her studies and not gotten married, Useaking says she would have liked to open her own sewing shop.
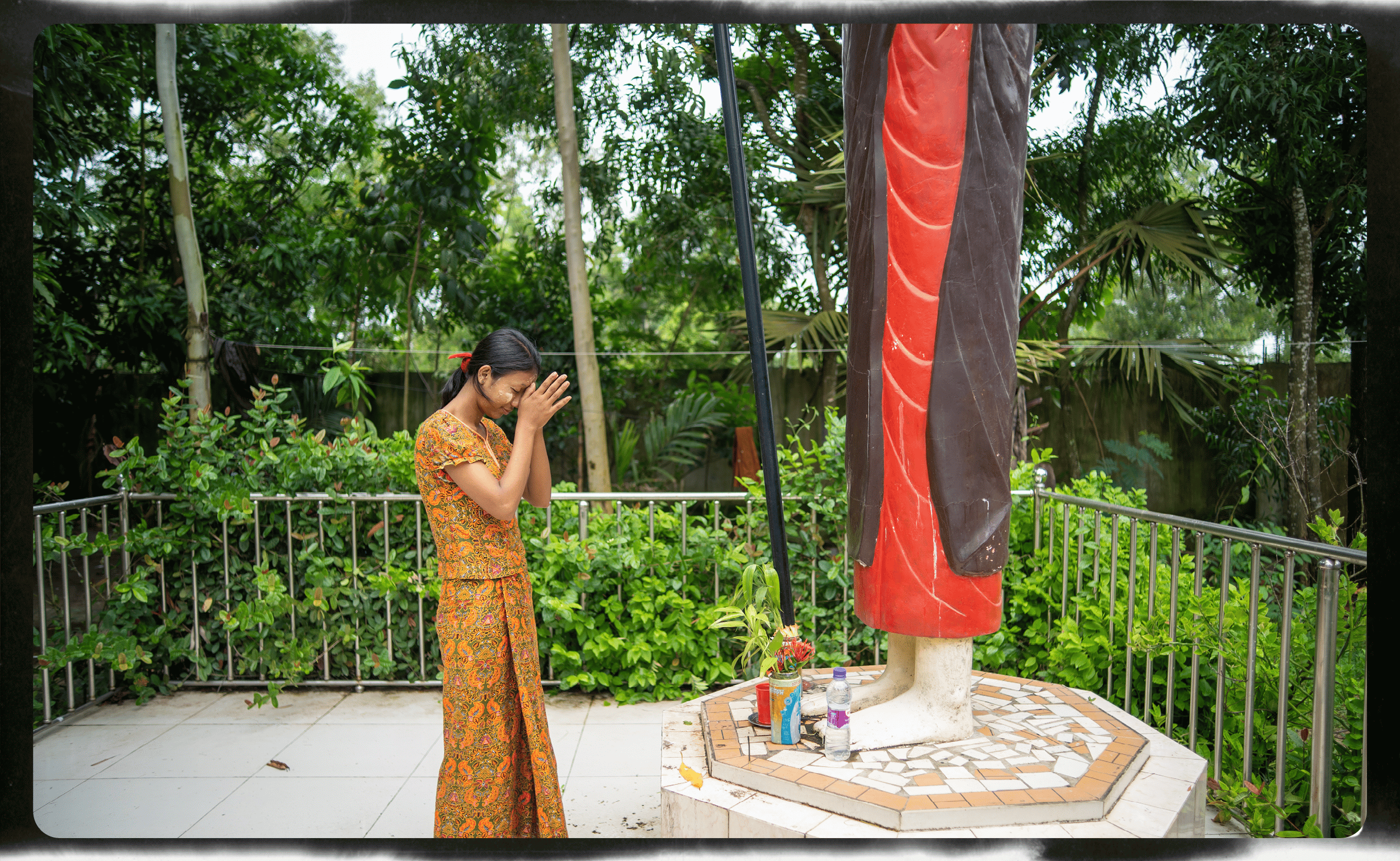
Giving thanks
Useaking’s daily routine involves a trip to a temple in her community in Cox’s Bazar to offer prayers.
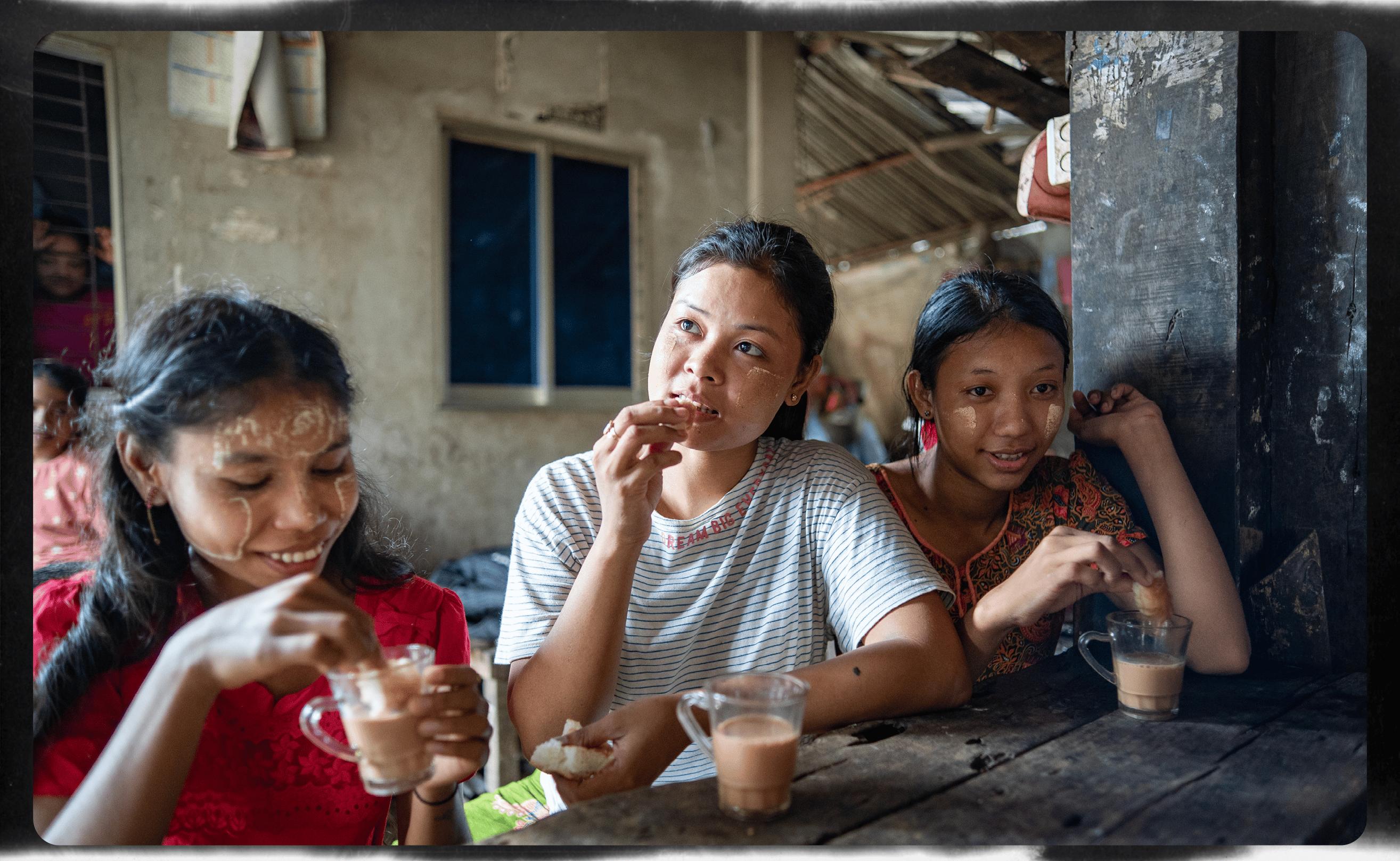
Tea time
Before she became a mother, Useaking loved having time for tea with her friends in the market. Now, the 21-year-old mother of two says it’s rare for her to have the freedom to be away from her children.
close


A stitch at a time
If she had continued her studies and not gotten married, Useaking says she would have liked to open her own sewing shop.
"
When Useaking was 16, she met a young man, and together a year later, they ran away and married. She thought it would bring her freedom. It didn’t. In our first-ever mini-doc filmed in Cox’s Bazar, discover how she’s ensuring that other girls keep their options open.
[Girls who study and work] can live freely and go wherever they want. If I had known, I might have made different choices.”
Photography by Tanveer Abid
"
When Useaking was 16, she met a young man, and together a year later, they ran away and married. She thought it would bring her freedom. It didn’t. In our first-ever mini-doc filmed in Cox’s Bazar, discover how she’s ensuring that other girls keep their options open.
[Girls who study and work] can live freely and go wherever they want. If I had known, I might have made different choices.”